Safe Mode is a diagnostic startup mode in Windows that loads only the essential drivers and services necessary for the operating system to function. It helps to troubleshoot issues that may be caused by third-party applications, corrupted system files, or hardware conflicts. When in Safe Mode, many of the usual startup programs and services are disabled, allowing you to isolate and address problems more effectively.
There are several reasons why you might need to use Safe Mode in Windows 10/11:
- Troubleshooting Software Issues: If a recently installed application is causing problems, Safe Mode can help you identify and remove it.
- Resolving Driver Conflicts: Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to system instability. Safe Mode can help you update or reinstall drivers without conflicts.
- Fixing Corrupted System Files: System files can become corrupted due to various reasons. Safe Mode can be used to run system scans and repair any damaged files.
- Removing Malware: Some malware can be difficult to remove in normal mode. Safe Mode can provide a clean environment to run antivirus scans and remove malicious software.
- Accessing Advanced Startup Options: Safe Mode can be used to access advanced startup options, such as System Restore, Command Prompt, and Startup Repair.
Why Use Safe Mode in Windows 10 or 11?
Safe Mode in Windows 10 and 11 is a diagnostic tool that starts your computer with only the essential drivers and services. Here are some key reasons to use it:
Troubleshooting Software and Driver Issues
Safe Mode is a valuable tool for diagnosing and resolving software and driver-related problems. By loading only essential system components, Safe Mode can help you identify which applications or drivers are causing conflicts or instability.
- Identifying Problematic Software: If your computer is experiencing frequent crashes or freezes, Safe Mode can help you determine if a recently installed application is the culprit. By booting into Safe Mode and disabling the suspect application, you can see if the issue persists.
- Resolving Driver Conflicts: Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to system instability and various errors. In Safe Mode, you can update or reinstall drivers without the interference of other running applications.
- Troubleshooting Startup Issues: If your computer is hanging during the startup process, Safe Mode can help you identify which programs or services are causing the delay and speed up your windows boot time . You can disable these items and see if the issue is resolved.
Removing Malware or Problematic Software
Malware, such as viruses, spyware, and ransomware, can infect your system and cause serious damage. Safe Mode provides a clean environment to run antivirus scans and remove malicious software.
- Running Antivirus Scans: In Safe Mode, antivirus software can scan your system more effectively, as many malicious programs are disabled.
- Removing Stubborn Malware: Some malware can be difficult to remove in normal mode. Safe Mode can help you manually delete or quarantine infected files.
- Preventing Malware from Loading: By booting into Safe Mode with Networking, you can disable network connections and prevent malware from spreading or downloading updates.
Diagnosing System Crashes
If your computer is frequently crashing, Safe Mode can help you isolate the root cause. By booting into Safe Mode and gradually enabling services and applications, you can identify which component is causing the instability.
- Identifying Hardware Conflicts: Hardware conflicts can lead to system crashes. By booting into Safe Mode with minimal drivers, you can determine if a hardware component is causing the issue.
- Troubleshooting Software Issues: As mentioned earlier, Safe Mode can help you identify software conflicts that may be causing system crashes.
- Checking for Corrupted System Files: System file corruption can also lead to crashes. In Safe Mode, you can run system scans to repair any damaged files.
By using Safe Mode effectively, you can troubleshoot and resolve a wide range of software and driver-related issues, remove malware, and diagnose system crashes.
Different Methods to Turn On Safe Mode in Windows 10 or 11
There are several ways to boot into Safe Mode in Windows 10 or 11, depending on your situation and preferences. Here are the most common methods:
How to Boot Into Safe Mode from Settings
- Open Settings: Click on the Start button and select “Settings.”
- Go to Update & Security: Click on “Update & Security.”
- Choose Recovery: Click on “Recovery.”
- Click on Advanced Startup: Under “Advanced startup,” click on “Restart now.”
- Select Troubleshoot: Choose “Troubleshoot.”
- Select Advanced Options: Click on “Advanced options.”
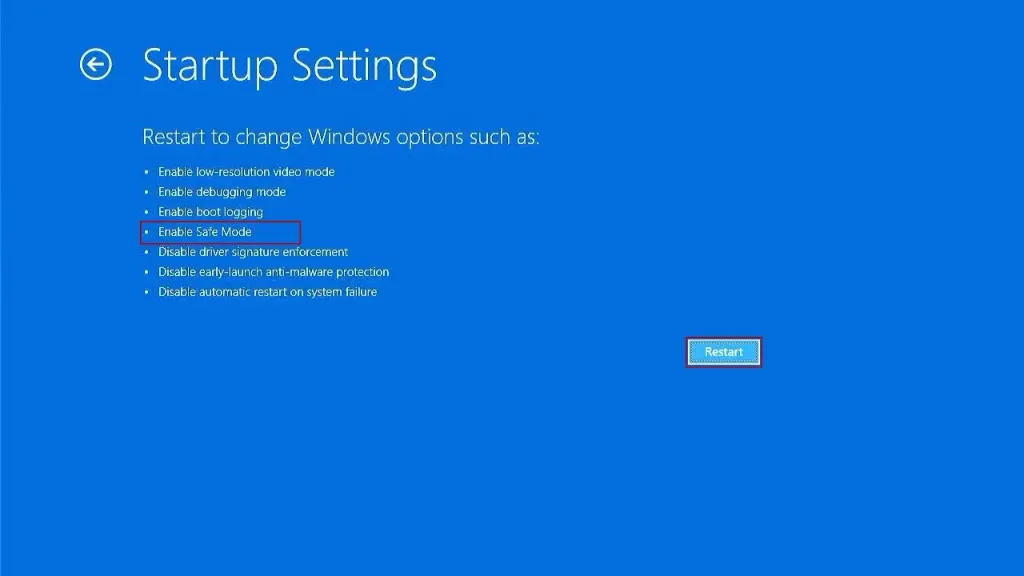
- Choose Startup Settings: Select “Startup Settings.”
- Restart Your Computer: Click on “Restart.”
- Choose Safe Mode: After your computer restarts, press the appropriate number key to select Safe Mode.
How to Use Shift + Restart to Enter Safe Mode
- Restart Your Computer: Click on the Start button and select “Power,” then choose “Restart.”
- Hold Shift: While your computer is restarting, hold down the Shift key.
- Select Troubleshoot: Choose “Troubleshoot.”
- Select Advanced Options: Click on “Advanced options.”
- Choose Startup Settings: Select “Startup Settings.”
- Restart Your Computer: Click on “Restart.”
- Choose Safe Mode: After your computer restarts, press the appropriate number key to select Safe Mode.
How to Enable Safe Mode Using System Configuration (msconfig)
- Open System Configuration: Press the Windows key + R, type “msconfig,” and press Enter.
- Go to the Boot Tab: Click on the “Boot” tab.
- Check Safe Boot: Check the “Safe boot” option.
- Choose Safe Mode Options: Select the desired Safe Mode option (e.g., Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Networking).
- Apply and Restart: Click on “Apply” and then “Restart.”
How to Enter Safe Mode from the Windows Sign-In Screen
- Restart Your Computer: Restart your computer.
- Repeatedly Press F8: As your computer is restarting, repeatedly press the F8 key.
- Choose Safe Mode: Select “Safe Mode” from the Advanced Boot Options menu.
Note: The exact key to press to access the boot options menu may vary depending on your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings.
. How to Boot into Safe Mode Using a Recovery Drive
- Insert Recovery Drive: Connect the recovery drive to your computer.
- Boot from Recovery Drive: Restart your computer and press the appropriate key to boot from the recovery drive (usually F12, Del, or Esc).
- Choose Troubleshoot: Select “Troubleshoot.”
- Select Advanced Options: Click on “Advanced options.”
- Choose Startup Settings: Select “Startup Settings.”
- Restart Your Computer: Click on “Restart.”
- Choose Safe Mode: After your computer restarts, press the appropriate number key to select Safe Mode.
Additional Safe Mode Options
In addition to the standard Safe Mode, Windows 10/11 offers several other options that provide different levels of functionality:
Safe Mode with Networking
This option enables network connectivity in Safe Mode, allowing you to access the internet and download updates or drivers. It’s useful for troubleshooting network-related issues or resolving problems that require online resources.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt
This option loads Safe Mode with the Command Prompt, a powerful tool for advanced system administration and troubleshooting. It’s useful for running system commands, repairing system files, or accessing hidden settings.
Safe Mode with Debugging
This option enables debugging tools, which can be used by developers or IT professionals to troubleshoot software and hardware issues at a low level. It’s generally not recommended for casual users.
By understanding these additional Safe Mode options, you can choose the most appropriate one for your specific troubleshooting nee
Exiting Safe Mode in Windows 10 or 11
How to Restart Normally:
- Restart from Start Menu: Simply click on the Start menu, select the Power button, and choose Restart. This should boot your computer back into normal mode if Safe Mode was a one-time boot.
- Using Shift + Restart: Hold the Shift key while selecting Restart from the Start menu. This will take you to the Advanced Startup Options menu. From there, navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Startup Settings > Restart. After the restart, select the option to boot normally.
- Or completely shutdown your laptop by following this guide
Using msconfig to Disable Safe Mode:
- Press
Win + Rto open the Run dialog box. - Type
msconfigand press Enter. - In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab.
- Uncheck the box next to Safe boot.
- Click Apply, then OK.
- Restart your computer.
This should help you exit Safe Mode and return to normal operation. If you encounter any issues or need further assistance, feel free to ask!
FAQs
To help you better understand Safe Mode and its use in Windows 10 and 11, we’ve compiled a list of frequently asked questions. These answers will provide more insight into how to use Safe Mode for troubleshooting, resolving computer problems, and maintaining system stability.

1. What is Safe Mode in Windows 10 or 11?
Safe Mode is a troubleshooting environment in Windows 10 and 11 that starts your computer with a minimal set of drivers and system files. It helps identify and fix issues like malware infections, software conflicts, and system crashes by isolating problematic software from the core system.
2. How do I know if my computer is in Safe Mode?
When your computer boots into Safe Mode, the words “Safe Mode” will appear in the four corners of your screen, and your desktop background will likely be black. The interface will also look more basic, with fewer features and no third-party applications running.
3. Can I use the internet while in Safe Mode?
Yes, but only if you boot into Safe Mode with Networking. This mode enables your network drivers and allows you to connect to the internet. This is useful when you need to download drivers, updates, or run online malware scans.
4. Why does my computer keep booting into Safe Mode?
If you entered Safe Mode using the msconfig (System Configuration) method and checked the Safe Boot option, your system will continue booting into Safe Mode until you uncheck it. To stop this, follow these steps:
1. Open msconfig and navigate to the Boot tab.
2. Uncheck Safe Boot and restart your computer to return to normal mode.
5. How do I exit Safe Mode and return to normal mode?
You can exit Safe Mode by simply restarting your computer. If you used msconfig to enter Safe Mode, you’ll need to disable it by unchecking Safe Boot in the System Configuration window before restarting.
6. Why would I need to use Safe Mode with Command Prompt?
Safe Mode with Command Prompt is used when you need advanced troubleshooting tools that are not available in the graphical user interface (GUI). It allows you to run system commands such as SFC, DISM, and chkdsk to fix issues like corrupted system files and hard drive errors.
7. Can I install or uninstall software in Safe Mode?
Yes, you can uninstall problematic software in Safe Mode, which is helpful when certain applications cause your system to crash or behave unexpectedly. However, installing software in Safe Mode can be tricky, as certain services required for installation may not be running.
8. Can Safe Mode help fix blue screen errors (BSOD)?
Yes, Safe Mode can help troubleshoot blue screen errors (BSOD). By booting into Safe Mode, you can isolate hardware or driver conflicts that might be causing the issue. You can also uninstall or update problematic drivers and run system diagnostic tools.
9. When should I use Safe Mode with Debugging?
Safe Mode with Debugging is an advanced option typically used by IT professionals and developers for kernel-level debugging. It’s not generally recommended for everyday troubleshooting, but it can be used for in-depth analysis of system crashes and hardware issues.
10. Is Safe Mode the same in Windows 10 and Windows 11?
Yes, Safe Mode operates similarly in both Windows 10 and Windows 11. The steps to enter and use Safe Mode, as well as the available troubleshooting options, are almost identical in both versions.
Conclusion
Safe Mode is a valuable tool for troubleshooting and resolving issues with your Windows 10/11 system. By understanding how to enter Safe Mode, its different options, and troubleshooting techniques, you can effectively address problems related to software, drivers, and system stability.
Remember to always follow the steps outlined in this guide carefully and seek professional help if you encounter persistent or severe issues. With proper troubleshooting and maintenance, you can keep your Windows system running smoothly and avoid major problems.
For a quick reference on how to enter Safe Mode in Windows 11, you can also visit the official Microsoft guide: How to Boot Safe Mode in Windows 11: https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/windows-11/how-to-boot-safe-mode-in-windows-11/td-p/2764802.